
Organisation
Handling acceleration, complexity and innovation requires rugged and flexible organisational structures. It is therefore desirable to have a lean, transparent and efficient high-performance organisation. Agile, dynamic units are important substructures.
Your needs
- You want to transform mature organisational structures that have become set in their ways and are embedded in a network?
- You want to implement innovative organisational concepts and avoid change for the sake of change?
- You want to ensure that new organisational principles are understood, internalised and implemented?
Our offer
We will help you to
- initiate change processes,
- clarify your vision and mission and
- successfully shape implementation processes.
Initial situation
The successful growth of a company, a new strategy or technical innovation will usually lead to new structures or restructuring.
An integrated organisational development process tightly interweaves structural and procedural changes with alterations in the behaviour of staff and executives.
Changes must therefore cover the "hard" as well as the "soft" dimension of the organisation: Structural change without cultural change results in idling: cultural change without structural change results in activism. What is needed is for the organisation to change direction and the people involved to change their way of thinking.
Familiar patterns of thinking and doing are to be questioned and structural and cultural changes are to be made in parallel. For the role-players - in particular those on the second level of leadership - this often means bidding farewell to cherished habits and spheres of influence.
Procedure
"Clean slates" and "thinking big" are helpful when it comes to handling the realignment of organisational units and divisions.
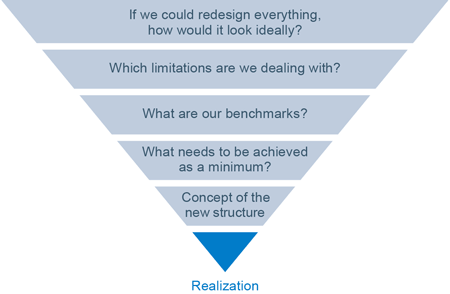
This clarification and discussion process must start in an open and generous framework in order to get to know the different views and to ensure a joint understanding of the alignment to be achieved.
Clarification to sound things out narrows the "funnel" and ultimately leads to a concept.
This method supports a resource-saving and efficient procedure. It prevents any topic from being discussed at any time and the discussion jumping between issues.
Targets
Increased and ever more complex customer requirements as well as increasingly difficult and very dynamic competitive situations require a critical examination of the essential business processes.
The aim is to develop innovative concepts for perfectly structuring internal procedures. The speed and reliability of the process are the key variables. Synchronisation, transparency and simplicity constitute the process visions.
In addition to the design of these processes, the associated changes of attitude among staff, their understanding of the new skills required and their synchronisation will play an important role.
Staff who are interested in change strive for quality and are orientated towards creating value: these are the key factors for the process vision when it comes to human potential.
Individual topics
- Establishment of a method for ongoing optimisation of the core processes, recognition of weak points and opportunities in the company processes, minimisation of "muda" and the efficient use of company resources
- Reducing and optimising interfaces
- Establishing a "toolbox" for continuous improvement
- Ongoing improvement of processes: synchronisation
- Further development and refinement of process management towards a "learning company"
Program
- Procedure for overall concept
- Workshop on "process optimisation"
- Creation and establishment of a decision-making committee
- Training of the moderators
- Coaching of the moderators with feedback
- Monitoring the results
- Instruments for stabilising the new processes
Targets
The effective and inspiring work of the team is an important aspect of a high-performance company culture. Positive thinking and open and constructive attitudes are the basis for successful team and project work.
However, whether and how the team members cooperate depends on compromises, clarifications and consistent framework conditions. The goal of team development is to support these clarifications in a systematic manner and to structure the framework conditions together in the spirit of continuous improvement.
The goal is to gain an overview, to approach one another and to intensify communication. Persons and organisational units with "closed doors" should again be included in contact and discussions.
Personal differences should be regarded as positive options, keeping opportunities in mind, so that liveliness, openness and creativity are reinforced.
Potentially critical situations
- Fragmentation
- Trench warfare
- Dull turbidity, negativism
- Intrigues, lack of respect
- Conflict-prone internal customer/supplier relationships
- Communities of believers", "sects"
- Elitist principalities
Concept: From team building via teamwork to the elite team
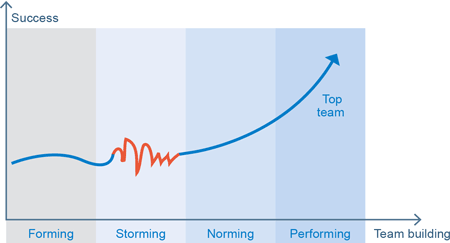
The procedure: Team orientation instead of team ideology
Team ideology creates unfulfillable expectations and assures frustration.
Leadership goals in the area of responsibility
Team orientation
- Self-responsibility within defined areas of responsibility
Team ideology
- Everyone has to be involved in everything
- Everyone has all the information
- Everyone knows everything
- The opinion of the supervisor is nevertheless enforced
Leadership goals in the personal area
Team orientation
- Skill development
- Feedback of personal tendencies
- Promote momentum
- Sich eingeordnet fühlen im Team
Team ideology
- We all like each other
- No one is allowed to hurt the other
Management method
Team orientation
- Goal-oriented Leadership in the team
- Emphasis on common and individual successes
Team ideology
- Prolonged promises
- Manipulative "we"
- Covert repression
- Cleavage: "If you've got that far then you can decide for yourself."
Ojectives
The goal is to ensure the implementation of strategic planning in realistic sales planning and consistently apply the Account Planning & Management method.
The aim is:
- Identify potential with major customers.
- To professionalize the understanding and processing of major customers.
- To complete the planning round with account reviews.
At the same time, the responsible executives should focus on analyzing the potential of each customer in a targeted manner at one place, at a table and at the same time, and plan measures to optimize the customer relationship and to realize the sales targets.
This planning should be systematically translated into KPIs.
In particular, it is important to understand the customer's strategy well, to be accepted as a strategic sparring partner in the planning of the customer and thus to be able to shape the customer's strategy.
The procedure
- Field analysis
- Preparation and follow-up of the workshops
- Execution of the workshops
- Control group
Starting point
The importance of project implementation has strongly increased due to the accelerated change process. There is no company that does not optimise its own project management.
However, it is surprising how many projects do not provide the desired results: postponed deadlines, higher costs and quality problems. It frequently happens that the wrong projects are initiated and the projects are not professionally handled.
According to an investigation of successful and failed software projects in the USA by the Standish Group, 31% of projects fail, 53% of projects are above the initial budget and only 16% are completed on time and on budget.
An investigation by Munich Technical University showed that approximately 30% of the total costs of a company are generated by project work - but that only one in eight projects adds value.
The reasons:
- Interaction between the organisation's units does not work
- Selection and qualification of the project managers: junior employees instead of professionals
- Composition of the team: time or "politics" instead of competence
- Order and target: "sheer madness" instead of realistic principles
- Implementation: taboos about problems instead of talking straight
Targets
Successful implementation of project work therefore strongly depends on whether there is a joint understanding of project management, to what extent the procedures are standardised and the skills of the project managers.
The goal is to:
- ensure a joint understanding of the project,
- establish lean, efficient and functional procedures,
- find suitable project managers,
- effectively structure conflict management,
- convey practically relevant knowledge for handling typical project situations.
The workshops:
- Workshop on "guidelines for project management"
- Team workshop on "project management and project work"
- Moderation and conflict solution for project leaders
- "Personality and project success"
